Last Updated on November 14, 2024 by Helena Akter
Are you feeling uneasy about the possible health risks linked to artificial food additives? Considering synthetic chemicals’ effects on health, it’s natural to wonder about their safety in food. And that concern brings up the question, are artificial food additives harmful for health?
Yes, artificial food additives are harmful to health. These additives include dyes, sweeteners, and preservatives, and they’ve been linked to health concerns like cancer and weight gain. For a healthier diet, make sure to inspect food labels and opt for less processed foods whenever possible.
In this article, we explore the latest studies on artificial food additives and their potential health hazards. Also, we’ll give you tips on how to consume less additives for the safety of you and your family. Thus, it’ll be easier for you to maintain a healthy diet with this knowledge.
Key Takeaways
- Artificial food additives such as dyes, sweeteners, and preservatives could lead to health problems like cancer and weight gain.
- Several prevalent artificial food additives, such as Artificial Food Dye, Artificial Sweeteners, BHA and BHT, Sodium Nitrite, Carrageenan, Aspartame, Sodium Benzoate, Monosodium Glutamate (MSG), High-Fructose Corn Syrup, and Xanthan Gum.
- These additives are associated with severe health problems like cancer, weight gain, negative effects on gut health, adverse impacts on children’s health, and hypersensitive reactions.
What is the Definition of Artificial Food Additive?
A food additive is any substance included in food as it’s made, processed, packaged, shipped, or stored. These artificial food additives serve various purposes, such as keeping food fresh, and improving its flavor, texture, look, or nutritional benefits.
List Of Harmful Chemicals In Food that Can Negatively Impact Your Health
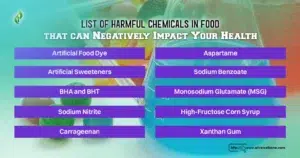
Let’s take a closer look at ten artificial food chemicals that research suggests could potentially impact our health negatively.
Artificial Food Dye
Artificial food additives brighten up the look of many processed items and drinks. Although most coloring agents are seen as harmless, certain ones could pose health issues. Specifically, Yellow 5, Blue 1, Yellow 6, and Red 40 have been linked to hyperactivity, behavioral changes, and allergic responses in kids.
Moreover, evidence indicates that Red 3 might raise tumor risks among animals. To steer clear of the harmful effects of food additives and preservatives, opting for natural foods and reducing intake of processed items with artificial colors is a wise choice.
Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners are one of the top artificial food additives examples. They’re served as sugar alternatives and are found in a variety of products. Some people might experience headaches, dizziness, or nausea from sweeteners such as aspartame, saccharin, and sucralose.
Research also hints that using artificial sweeteners over time could heighten the chances of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. In case you’re dealing with obesity, there are healthy foods that can help you with your weight loss goals.
BHA and BHT
BHA and BHT are additives used to keep processed foods fresh by preventing spoilage. Some research has raised concerns that these substances could be cancerous in animals, though it’s not yet clear if they affect humans in the same way.
Sodium Nitrite
Sodium Nitrite keeps meats fresh, adds a salty taste, and turns them pink. But, when cooked at high temperatures or combined with certain amino acids, it can form nitrosamine, which is harmful and has been linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer.
Also, many studies suggest that eating a lot of processed meats, preserved with nitrites, increases the chances of colorectal, breast, and bladder cancers.
Carrageenan
Carrageenan acts as a thickener in foods like dairy products and salad dressings. It’s been debated for years over its safety and possible health effects. One study on animals found that carrageenan could raise blood sugar levels and make the body less able to handle glucose, particularly alongside a high-fat diet.
It’s also thought to harm digestive health, potentially causing intestinal ulcers and growths. However, we need more research to fully understand carrageenan’s impact on humans.
Aspartame
Aspartame is a low-calorie sweetener, often found in blue packets, used in various foods and drinks like gum, cereals, soft drinks, and dairy products. The FDA approved it in the 1980s. It’s not used in baked goods because heating it causes it to lose its sweetness.
Aspartame is considered a safe sugar alternative for people with diabetes because it doesn’t significantly affect blood sugar levels. Despite concerns, there’s no conclusive evidence linking aspartame to cancer. However, some people might get headaches from aspartame, so if it bothers you, avoiding it might be wise.
Sodium Benzoate
As a preservative, sodium benzoate is added to fizzy drinks and acidic foods such as dressings, pickles, and juices. The FDA considers it safe, but some research suggests it could have side effects.
For instance, one study found that college students who drank more beverages with sodium benzoate had higher rates of ADHD symptoms. Another study observed an increase in hyperactivity among 3-year-olds who consumed sodium benzoate and artificial food coloring together.

Fizzy drinks, especially those that are diet or sugar-free, tend to have the most benzene, a compound that can form in drinks with sodium benzoate.
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is a flavor enhancer that adds a savory taste to food. It comes from glutamic acid, which is an amino acid found naturally in many foods and also in our bodies.
To make MSG, manufacturers ferment starch, sugar, or molasses, using a process similar to how yogurt or wine is made. Since the 1960s, some people have reported negative reactions to MSG in food, sparking debates about its safety.
Research on MSG’s safety has produced mixed results. For instance, one study suggests that consuming MSG regularly might increase blood pressure in some cases, though more studies are needed to confirm this.
While MSG doesn’t seem to harm most people, individual reactions, like sensitivity to MSG, can occur. Interestingly, research also shows MSG might lower the risk of high blood sugar in some cases.
If you think you’re sensitive to MSG, considering reducing it in your meals might help.
High-Fructose Corn Syrup
High-Fructose Corn Syrup (HFCS) is a common sweetener found in many processed drinks, foods, and desserts. It’s loaded with fructose, a type of sugar that can be harmful in large quantities. Research links HFCS to an increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes.

But if you’re worried about your cardiovascular system, you can eat heart-healthy foods to minimize the risk of heart disease.
In one study, people who drank beverages sweetened with fructose gained more belly fat their blood sugar levels increased and their insulin sensitivity decreased. This highlights why are food additives bad for you, especially when consumed excessively.
Xanthan Gum
Xanthan Gum is widely used to thicken and stabilize foods like dressings, soups, and sauces. While it’s connected to some health benefits, research into these advantages is still in its early stages.
Eating a lot of xanthan gum could lead to digestive issues, including more frequent bowel movements, gas, and softer stools. However, for most individuals, xanthan gum is considered safe and causes no problems.
If you notice any adverse effects after consuming xanthan gum, reducing your intake or cutting it out of your diet might be a good idea.
What are the Harmful Effects of Food Additives?

Even with strict safety checks, some people are concerned about the long-term health impacts of artificial food additives.
Cancer
Cancer risk is one concern linked to certain additives. Foods high in nitrites and nitrates, often found in processed meats, could increase colorectal cancer risk. Bisphenol A (BPA), used in some food packaging, is associated with cancer and hormonal issues.
While it’s no longer used in baby products, you can still find it in various containers.
There’s limited proof that other food additives directly lead to cancer. However, eating a lot of processed foods, which often contain these additives, is linked to a higher cancer risk. The exact role of food additives in this risk remains uncertain.
Weight gain
Many people turn to artificial sweeteners—a common type of food additive—as a low-calorie alternative to sugar. These sweeteners, including well-known types like aspartame, saccharin, acesulfame K, and sucralose, add sweetness without adding calories.
Even though they don’t have calories, there’s a theory that artificial sweeteners might lead to weight gain by affecting your gut health, metabolism, and hormones. However, these sweeteners generally don’t reach the part of your gut where microbes live.
So, it’s doubtful they impact your gut microbiome. Indeed, no research has definitively proven that artificial sweeteners cause weight gain. That said, you can opt for either running or walking for overall health improvement.
Gut health
So far, there’s not much proof that artificial food additives, which the FDA has deemed safe, damage your gut health or digestion. However, with more people getting gut disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn’s disease, and eating more processed foods, some are asking if there’s a link to additives.
Early studies in mice show that artificial sweeteners might reduce the variety of gut bacteria, possibly causing digestive problems. But, it’s important to remember that our bodies process things differently than animals’. Plus, these studies often use much higher amounts of sweeteners than what people typically eat.
So, we need more research to understand fully.
Children’s Health
There’s debate over whether certain artificial food additives, like food colorings, cause conditions like attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Artificial colorings and flavorings make many kid-friendly foods more appealing.
Despite claims from diets like the Feingold diet that these additives can cause behavioral or developmental issues, there’s little scientific evidence to back this up.
Hypersensitive Reactions
Some people might react badly to food additives, experiencing a range of symptoms. These can include digestive troubles like diarrhea, nervous issues such as trouble sleeping and hyperactivity, breathing difficulties including asthma, and skin problems like hives.
It’s hard to say how often these reactions happen or exactly why, as the studies we have are old and not very reliable. Figuring out if a food additive is causing these problems can be tough, and sometimes, avoiding foods with these additives is the best solution.
List of 6 Food Additives Banned Outside of the U.S.

We have compiled a list of the top artificial food chemicals that have been banned outside the U.S., you should know about.
Brominated Vegetable Oil
BVO is a flavoring additive used in some sodas to keep the flavor mixed in. However, bromine, a component of BVO, can irritate the skin and inside of the mouth and lead to issues like memory loss, headaches, and problems with nerves over time.
Research has found that bromine can accumulate in your body. Because of these concerns, BVO has been banned in countries like Japan, India, and the European Union.
Titanium dioxide
Titanium dioxide is a chemical often added to food in the U.S., though it might not be obvious from reading food labels. Instead of saying titanium dioxide, labels might use terms like “artificial color.” It means you could be eating it in various foods without knowing.
Common foods with titanium dioxide include —
- Gum
- Candies
- Cottage cheese
- Sweets
- Soups
- Cake icing
- Alcoholic drinks
- Sauces and other processed foods.
While it’s banned in the European Union due to health concerns like a potential link to lung cancer, more studies are needed to understand the risks fully. Despite this, titanium dioxide is still found in foods in Canada and the U.S.
However, California banned products like Skittles in 2023 for using titanium dioxide and other additives.
Ractopamine
Ractopamine is a drug given to livestock to help them gain weight more efficiently. Plus, research indicates it can make animals more agitated and stressed. While many countries, including Russia, Taiwan, China, and the European Union, have banned its use, the United States still allows it.
BHA and BHT
These chemicals are used as preservatives in a lot of foods in the U.S., including
- Breakfast cereals like Kellogg’s Apple Jacks
- Pillsbury cake mix
- Stouffer’s Frozen pizza
- Jiffy Corn Muffin Mix
- Bugles corn chips
The European Union has banned BHA and BHT because animal studies suggest they could increase cancer risk

However, studies in humans are not conclusive, and more research is needed. Brands like Kellogg’s, Jiffy, Stouffer’s, and Pillsbury use these preservatives to make their products last longer on the shelves.
It’s a good idea to read food labels to see if these chemicals are in your food.
Potassium Bromate
Potassium Bromate is used in the U.S. to make bread rise. It has been linked to cancer in animal studies and is considered a possible cancer risk to humans. As a result, countries like Brazil, China, the U.K., and India have banned it.
rbST
rbST, also known as recombinant bovine somatotropin, is a man-made hormone similar to the natural growth hormone in cows. Its main use is to boost milk production in dairy cows.
While it’s unclear if rbST directly affects human health, studies have shown it can lead to health issues in cows. These include problems with their legs and hooves, infections in the udder, infertility, and birth defects. Due to these concerns, countries like the Canada and European Union have banned rbST.
Tips to Reduce the Intake of Artificial Food Additives
If you want to minimize your consumption of artificial food additives, here are some effective tips that will help.
Check the Ingredient Labels
While shopping, take a moment to look at product labels closely. You’ll find that many brands are now making versions of their products with fewer artificial food additives. Watch out for sneaky additives like silicon dioxide in your spices or polysorbate 80 in dairy items.
Eat Minimally Processed Foods
If you want to eat less processed food, go for fresh whole grains, produce, and nuts. Besides, cooking your meals from scratch gives you control over the ingredients you’re eating.
Buying your produce at farmers’ markets or through a CSA program is a great choice for finding fresh and less processed options.
Switch Things Around
Here are some easy changes you can make —
- Use an air popper for your popcorn instead of microwave bags.
- Season with fresh herbs and spices rather than using store-bought marinades and sauces.
- Pick real butter over margarine.
- Choose block cheese instead of pre-shredded cheese.
- Sweeten with natural options like honey or maple syrup, rather than artificial pancake syrups.
- Customize plain yogurt with your own nuts or fruit, instead of buying flavored yogurt.
- Opt for plain chips and crackers rather than flavored ones.
Be Creative in Your Kitchen
In the kitchen, be inventive by making your own salad dips, dressings, or taco mixes. Plus, flavor your sparkling water with fresh citrus or herbs. For holiday baking, use natural colors like beet juice for red icing and matcha for green icing.
For more information about food additives, you can check out resources from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Artificial Food Conclusion
Are artificial food additives harmful to health? Yes, artificial food additives, like dyes, sweeteners, and various preservatives including BHA, BHT, Sodium Nitrite, and others, are common in our food. Especially in children, these additives can cause health issues such as cancer, weight gain, and problems with gut health.
Now, remembering these additives and their effects is important for your health. Plus, you must try your best to consume fewer harmful additives. For that reason, read food labels, choose foods that are barely processed, eat a variety of natural foods, and cook more at home.
By following these tips, you can reduce the amount of artificial additives in your diet and live a healthier life.
Artificial Food FAQs
Are food additives safe?
The majority of artificial food additives are not harmful to our health. Those that could pose health risks are either banned or regulated by the FDA. Instead of avoiding artificial additives, switch to more whole, minimally processed foods. It’ll naturally reduce your intake of these additives.
How do I find out which additives are in foods?
When manufacturers add substances directly to food, they must list them on the ingredient labels, often using scientific names. For instance, instead of saying salt, the label might say sodium chloride. Sugar could appear as sucrose and vitamin C as ascorbic acid. Artificial colors typically show up as numbers like Blue #2 or Yellow #5.
However, it’s tricky with indirect additives that come from the food’s packaging or processing, like chemicals from plastics, glues, dyes, and papers. These aren’t listed on labels but can still make their way into food.
What food additives cause inflammation?
Enhancers like monosodium glutamate can cause chronic inflammation and affect liver health. Similarly, artificial sweeteners like aspartame and food coloring may also lead to inflammation.
What is the number 1 food additive in the United States?
Out of over 3,000 additives used, sugar, salt, and corn syrup top the list as the most frequent ones in American foods.
What are the risks of plastic additives?
Chemicals like Bisphenol A (BPA), found in plastics, are believed to mess with our hormonal balance. This exposure is linked to about 80 different health issues, including cancer, obesity, and fertility problems.







